Navigating the Journey: From Prototype to Production – The Medical Device Development Process
The world of medical device development is a complex and highly regulated landscape where innovation meets stringent safety and efficacy standards. From the initial spark of an idea to the final market-ready product, the journey from prototype to production involves multiple stages that demand careful planning, meticulous execution, and close collaboration among various stakeholders. In this article, we delve into the intricacies of the medical device development process, shedding light on the key stages, challenges, and considerations that guide this transformative journey.
Table of Contents
Medical Device Conceptualization and Ideation
The journey begins with a vision for a new medical device or an enhancement of an existing one. This could stem from a clinician’s observation of a gap in patient care, an engineer’s breakthrough innovation, or even a collaboration between interdisciplinary teams. The process involves brainstorming, research, and market analysis to ensure the proposed device meets a real clinical need and has a potential market.
Proof of Concept and Prototype
Once the idea is solidified, the next step involves creating a proof of concept and developing prototypes. Proof of concept verifies that the basic principles of the device are feasible. Prototypes, on the other hand, are tangible models that showcase the device’s form and function. These iterations allow engineers to identify design flaws, technical challenges, and refine the concept accordingly.
Design and Development
During this phase, the initial prototype is transformed into a detailed design with specifications, materials, and manufacturing processes defined. This stage often involves multiple iterations, simulations, and feasibility studies to ensure the device meets regulatory standards, usability requirements, and safety guidelines.
Regulatory Compliance and Preclinical Testing
Medical devices are subject to rigorous regulatory oversight to ensure patient safety and device effectiveness. Before moving to clinical trials, thorough preclinical testing is conducted. This involves bench testing, animal studies, and in vitro assessments to gather data on the device’s safety and performance. The results of these tests are submitted to regulatory bodies as part of the approval process.
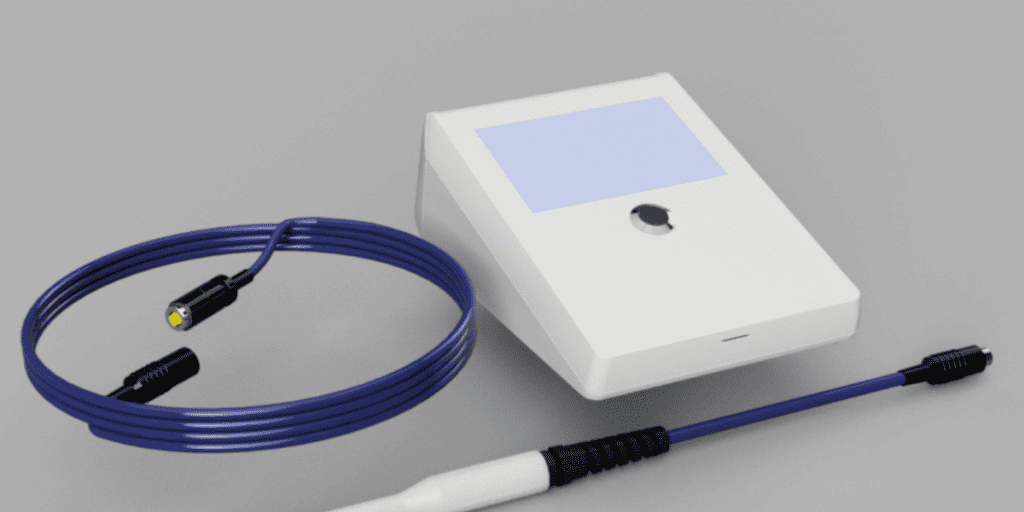

Clinical Trials
Clinical trials are a critical stage in medical device development. These trials involve human subjects and are conducted in multiple phases to evaluate the device’s safety, efficacy, and performance in real-world scenarios. Data collected from these trials play a pivotal role in securing regulatory approvals.
Regulatory Submission and Approval
Once clinical trial data is collected and analyzed, the manufacturer compiles a comprehensive regulatory submission, including evidence of safety and efficacy. This submission is reviewed by regulatory agencies, such as the FDA in the United States or the CE Mark in Europe. Approval signifies that the device can be marketed for its intended use.
Manufacturing and Quality Control
With regulatory approval in hand, manufacturing processes are scaled up for commercial production. Quality control measures are implemented to ensure consistency, reliability, and adherence to design specifications. This stage also involves developing post-market surveillance plans to monitor the device’s performance once it’s in the hands of users.
Market Launch and Post-Market Activities
The device is now ready for market launch. Marketing strategies, distribution channels, and training materials are developed to introduce the device to healthcare professionals and end-users. Post-market activities include ongoing monitoring of the device’s performance, addressing user feedback, and making necessary improvements..
Conclusion
The journey from prototype to production in medical device development is a meticulous and multifaceted process that demands innovation, precision, and adherence to regulatory standards. Through stages of conceptualization, design, testing, regulatory compliance, manufacturing, and post-market surveillance, interdisciplinary collaboration is essential for success. This process not only transforms groundbreaking ideas into tangible solutions but also ensures that the devices entering the market are safe, effective, and capable of improving patient care.